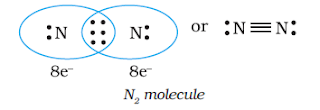chemical bonding and molecular structure
Wednesday, 6 September 2017
· 1 comments
Molecule :
A group of atoms is found to exist together as one species having characteristic properties. Such a group of atoms is called a molecule.
Chemical Bond :
The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond.
KÖSSEL-LEWIS APPROACH TO CHEMICAL BONDING :
Lewis given the concept of stable valence shell by considering nucleus and inner electron as a kernel and outermost shell around it.so that all eight electron occupy
eight corners of cubic lattics and outermost shell tend to get inert gas configuration by gaining or losing electrons.Lewis also postulated that atoms achieve the
stable octet when they are linked by chemical bonds
Lewsis symbols :
Valence electrons : In the formation of a molecule, only the outer shell electrons take part in chemical combination and they are known as valence electrons.
Lewis has given symbol method to represent outermost shell of all elements of periodic table for example :-
Lewsis symbols for elements of second period is given below :
significance of lewis symbols :
The dots represent number of valence electrons and it helps to calculate group valence electrons
Group Valence electrons :
The group valence of the elements is generally either equal to the number of dots in Lewis symbols or 8 minus the number of dots or valence electrons.
Kössel, in relation to chemical bonding,drew attention to the following facts:
• In the periodic table, the highly electronegative halogens and the highly electropositive alkali metals are separated by the noble gases.
• The formation of a negative ion from a halogen atom and a positive ion from an alkali metal atom is associated with the gain and loss of an electron by the
respective atoms.
• The negative and positive ions thus formed attain stable noble gas electronic configurations. The noble gases (with the exception of helium which has a duplet
of electrons) have a particularly stable outer shell configuration of eight (octet) electrons, ns2np6.
• The negative and positive ions are stabilized by electrostatic attraction.
Let us take example of formation of Nacl:-
Electrovalent Bond :
The bond formed, as a result of the electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions was termed as electrovalent bond.The electrovalence
is thus equal to the number of unit charge(s) on the ion.
Octet Rule :
According to this,atoms can combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another (gaining or losing) or by sharing of valence electrons in order to have an octet in their valence shells. This is known as octet rule.
Covalent Bond :
Sharing of electron to attain noble gas configuration leads to formation of covalent bond.for example chlorine formed by sharing a pair of electron among two chlorine atoms
The dots represent electrons. Such structures are referred to as Lewis dot structures.
The important conditions Lewis dots are :
• Each bond is formed as a result of sharing of an electron pair between the atoms.
• Each combining atom contributes at least one electron to the shared pair.
• The combining atoms attain the outershell noble gas configurations as a result of the sharing of electrons.
If two atoms share two pairs of electrons, the covalent bond between them is called a double bond
When combining atoms share three electron pairs as in the case of two nitrogen atoms in the N2 molecule and the two carbon atoms in the ethyne molecule, a triple bond is formed.
A group of atoms is found to exist together as one species having characteristic properties. Such a group of atoms is called a molecule.
Chemical Bond :
The attractive force which holds various constituents (atoms, ions, etc.) together in different chemical species is called a chemical bond.
KÖSSEL-LEWIS APPROACH TO CHEMICAL BONDING :
Lewis given the concept of stable valence shell by considering nucleus and inner electron as a kernel and outermost shell around it.so that all eight electron occupy
eight corners of cubic lattics and outermost shell tend to get inert gas configuration by gaining or losing electrons.Lewis also postulated that atoms achieve the
stable octet when they are linked by chemical bonds
Lewsis symbols :
Valence electrons : In the formation of a molecule, only the outer shell electrons take part in chemical combination and they are known as valence electrons.
Lewis has given symbol method to represent outermost shell of all elements of periodic table for example :-
Lewsis symbols for elements of second period is given below :
significance of lewis symbols :
The dots represent number of valence electrons and it helps to calculate group valence electrons
Group Valence electrons :
The group valence of the elements is generally either equal to the number of dots in Lewis symbols or 8 minus the number of dots or valence electrons.
Kössel, in relation to chemical bonding,drew attention to the following facts:
• In the periodic table, the highly electronegative halogens and the highly electropositive alkali metals are separated by the noble gases.
• The formation of a negative ion from a halogen atom and a positive ion from an alkali metal atom is associated with the gain and loss of an electron by the
respective atoms.
• The negative and positive ions thus formed attain stable noble gas electronic configurations. The noble gases (with the exception of helium which has a duplet
of electrons) have a particularly stable outer shell configuration of eight (octet) electrons, ns2np6.
• The negative and positive ions are stabilized by electrostatic attraction.
Let us take example of formation of Nacl:-
Electrovalent Bond :
The bond formed, as a result of the electrostatic attraction between the positive and negative ions was termed as electrovalent bond.The electrovalence
is thus equal to the number of unit charge(s) on the ion.
Octet Rule :
According to this,atoms can combine either by transfer of valence electrons from one atom to another (gaining or losing) or by sharing of valence electrons in order to have an octet in their valence shells. This is known as octet rule.
Covalent Bond :
Sharing of electron to attain noble gas configuration leads to formation of covalent bond.for example chlorine formed by sharing a pair of electron among two chlorine atoms
The dots represent electrons. Such structures are referred to as Lewis dot structures.
The important conditions Lewis dots are :
• Each bond is formed as a result of sharing of an electron pair between the atoms.
• Each combining atom contributes at least one electron to the shared pair.
• The combining atoms attain the outershell noble gas configurations as a result of the sharing of electrons.
If two atoms share two pairs of electrons, the covalent bond between them is called a double bond
When combining atoms share three electron pairs as in the case of two nitrogen atoms in the N2 molecule and the two carbon atoms in the ethyne molecule, a triple bond is formed.